
The so called Klenow fragment is one such molecule that is widely used in recombinant DNA work. Each of its three enzymatic activities are located into distinct domains of the holoenzyme, such that proteolytic deletions can be generated that lack one or more of the activities.

It is a single-chain protein that requires magnesium as a cofactor. This is the first DNA polymerase enzyme isolated by Kornberg having molecular weight of 109 KD.
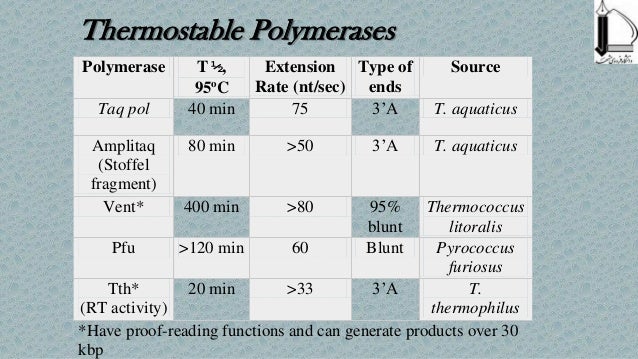
The holoenzyme is a dimer with two active sites, one for synthesizing the leading strand and one for extending the lagging strand. The holoenzyme attaches firmly to the template and move along with the leading strand until the synthesis is complete. There are only 10-15 holoenzyme molecules per cell. The mitochondrial DNA polymerase is like Ƴ polymerase. The polymerase copies many poly ribo-nucleotides such as poly (A) and poly (C). The β polymerase copies a poly (A) or poly (C) template. The α and β polymerases are located in the nucleus. These are present in the holoenzyme in equal ratio. Besides these, there are smaller subunits like, , χ % and Ѱ (Table 13.1).Įukaryotes have ten DNA polymerases, which in mammals are distinguished by Greek suffixes. The three main subunits which form the core enzyme are called α, ɛ and θ, with the polymerase activity carried out by a subunit and 3′ → 5′ exo-nuclease activity by ɛ. DNA polymerase I and II are single polypeptides, but DNA polymerase III is a ten subunits protein with a molecular mass of approx. Now we know that DNA polymerase III, isolated in 1972, is involved in replication along with DNA polymerase I. Later on it was named as DNA polymerase I after the discovery coli by Arthur Romberg in 1957, which was also called as Korenberg polymerase. However, this activity is required by the enzyme to remove already attached small DNA fragments on the template (during ligation of Okazaki fragments). (b) A 5′ 3′ exonuclease activity is less common. It is called as proofreading activity and enzyme corrects the error by removing the mismatch nucleotide. This activity enables the enzyme to remove nucleotides from the 3′ end of the strands that it has just synthesized. (a) A 3′ 5′ exonuclease activity is shown by template dependent DNA polymerases. This enzyme can add as well as remove polynucleotide (exonuclease activity): This enzyme is also called as replicase when it replicates the DNA molecules. DNA polymerases carry out the process of addition of nucleotides and formation of polynucleotide chain. The principal chemical reaction catalysed by a DNA polymerase is the 5′ 3′ synthesis of a DNA polynucleotide. It also describes the role of different types of eukaryotic polymerases in DNA synthesis. This article provides a close look on the DNA Polymerase enzymes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
